CNC ASSOS MOTE
CNC ASSOS MOTE
Modern CNC machines (numerical control) are complex mechanisms that allow you to create parts with high accuracy. But behind this accuracy and complexity is a simple, but very important concept - the movement of the axes. Let's figure out what it is and how it works.
The main types of axes
The axis of the machine, like the hands of a person, have a certain range of movement. They can move linearly, that is, directly, or rotate. Most often, CNC machines have three main linear axes (X, Y, Z) and often another rotation axis (for example, A), which can additionally rotate the workpiece. Imagine how the builder moves the instrument in space: the right and left (x), forward-back (y), up and down (Z). The rotational movement (axis a) allows you to process complex surfaces, as if rotating the part on the emery circle. Each of these movements is performed with high accuracy, thanks to the exact drives and control system.
Oxes interaction to achieve the result
Consistent and accurate movements along all axes are the key to creating the right part. The program setting the work of the machine describes all these movements. For example, to create a hole, the program will indicate at what point of the X, Y, Z axis you need to start drilling, and at what speed and depth this drilling should occur. The machine control system, like a skilled mechanic, performs these commands, accurately moving tools and the processed part. Each team received from the operator should be clear and accurate to avoid errors.
Accuracy and speed in work
The movement of the axes of the CNC machine directly affects the quality and speed of processing parts. High accuracy of the axes allows you to create parts with a given geometry and sizes with minimal deviations. The speed of the axes determines the processing speed and productivity of the machine. Modern machines are able to perform very complex and accurate operations in a matter of minutes, which makes them indispensable in modern production. The final quality of the product depends on how accurately and quickly the axis moves.
AppropriateProducts
Corresponding products
The best soldproducts
The best -selling products-
 Taisin Metal 3D printer ISLM600QN
Taisin Metal 3D printer ISLM600QN -
 Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA550Lite
Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA550Lite -
 Taisin Light-adopted 3D printer SLA1300D
Taisin Light-adopted 3D printer SLA1300D -
 Taisin drilling and threaded-cutting machine with CNC TXT-700
Taisin drilling and threaded-cutting machine with CNC TXT-700 -
 Taisin high-speed drilling and threaded machine TX-T6
Taisin high-speed drilling and threaded machine TX-T6 -
 Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA300
Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA300 -
 Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA200
Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA200 -
 Taisin horizontal processing center YBM-1270
Taisin horizontal processing center YBM-1270 -
 Taisin Light-adopted 3D printer SLA660Lite
Taisin Light-adopted 3D printer SLA660Lite -
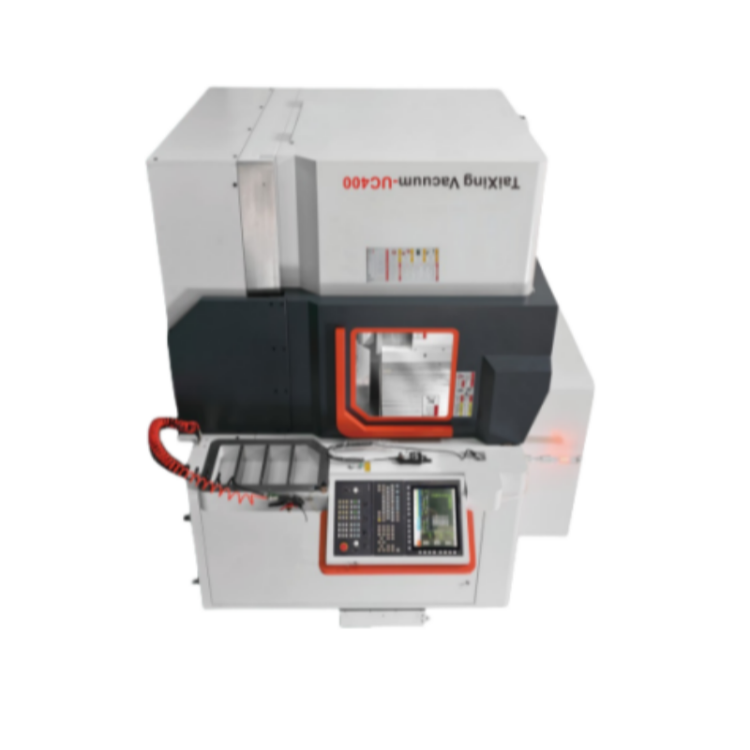 Taisin high-speed five-axis processing center TX-UC400
Taisin high-speed five-axis processing center TX-UC400 -
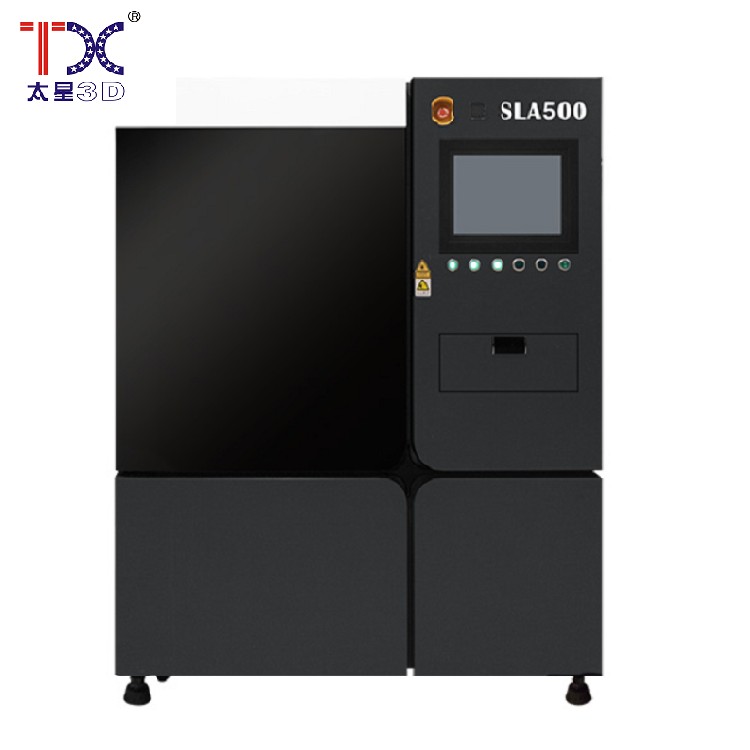 Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA500
Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA500 -
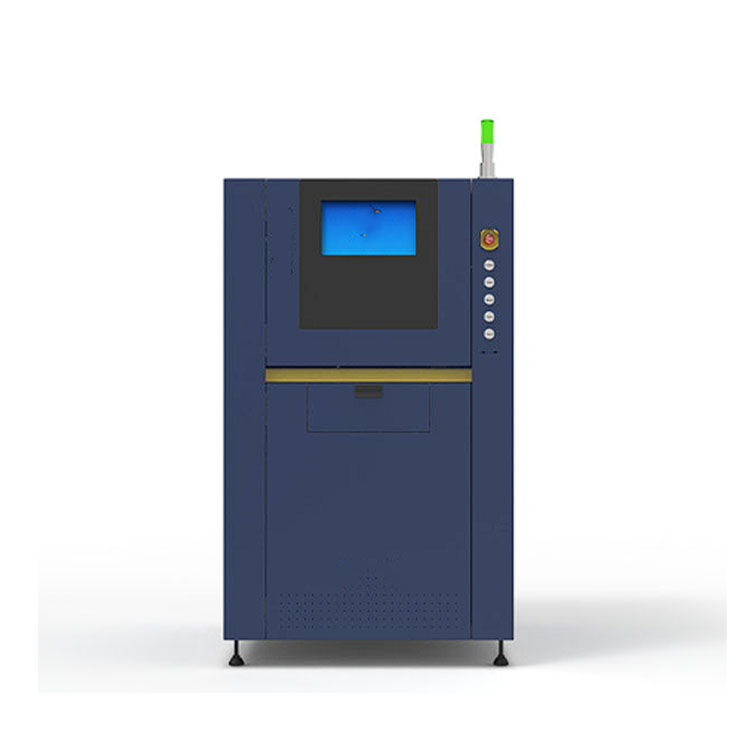 Taisin Metal 3D printer SLM160
Taisin Metal 3D printer SLM160
Connectedsearch
Related search- Suppliers of educational 3D printing in China
- Cheap SLA suppliers Print (stereolithography)
- Cheap 5 axes of CNC machines suppliers
- Factory for DLP printing (digital light processing) in China
- Cheap selective laser melting (SLM) Suppliers
- Cheap four axes of CNC manufacturers
- OEM suppliers 5-axial milling machines with CNC
- Cheap 3D printing factories
- CNC 2 axis
- Cheap suppliers Sing -axic CNC machines











