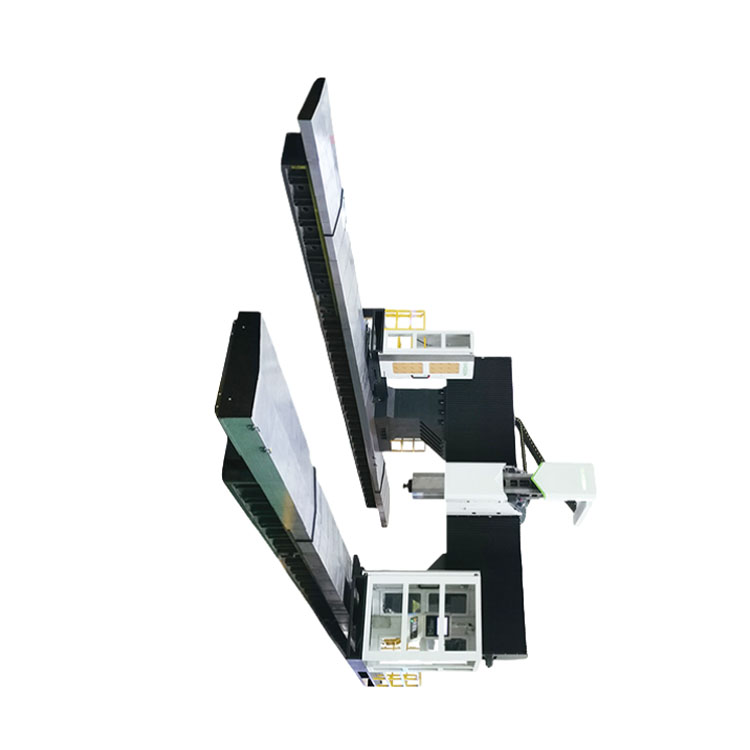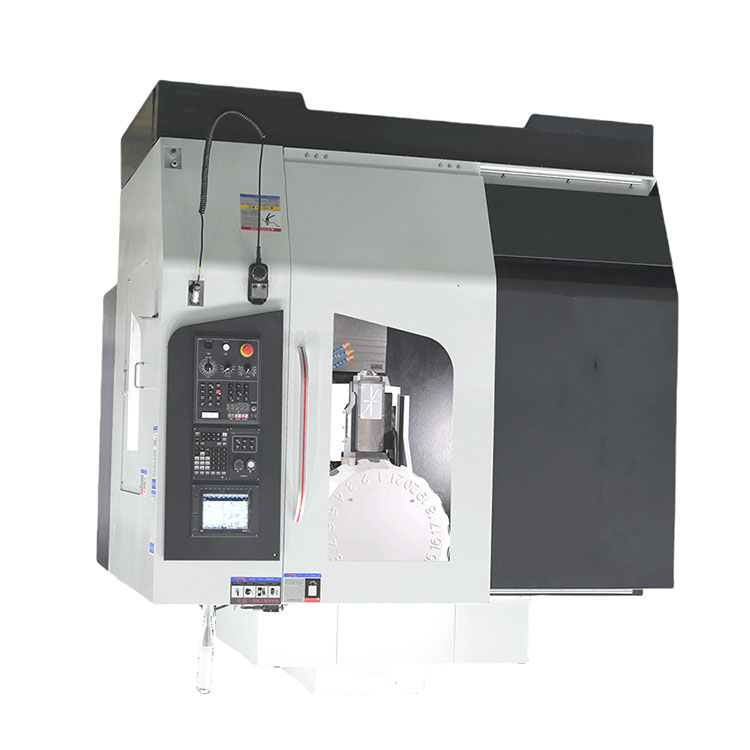
CNC axis
CNC axis: how it works and why it is needed
The CNC axis (numerical management) is the heart of many modern production machines. Imagine a lathe, a milling center or a 3D printer. All of them, one way or another, use the CNC axes to perform complex tasks for processing materials. But what is this axis?, And why is it so important?
How does the CNC axis work?
The CNC axis is based on electronics that controls the movement. Imagine a complex computer program that gives clear instructions. These instructions describe the exact position, speed and direction of the tool (for example, the cutting tool on the lathe). Electric motors and control systems drive the axis, allowing the tool to accurately repeat the specified paths. It is this accuracy and repeatability that allow you to create complex parts with high accuracy.
Why do you need a CNC axis?
The advantage of the CNC axis in its ability to perform complex and repeated operations. Without CNC, for example, the creation of each part would be a manual process that requires great skill and time. With CNC, the machine repeats the given operation again and again with unchanging accuracy. This allows:
Increase the speed of production: the machine works much faster than a person, which reduces the time to make parts.
Increasing accuracy: CNC machines provide the highest accuracy of processing, which is extremely important for creating parts that require a high degree of Precision (for example, in hourly production or aircraft industry).
Reduce the number of errors: the repeatability of operations minimizes human errors, which improves the quality of finished products.
Creating complex forms: CNC allows you to create details with incredibly complex forms that can not be performed manually.
Advantages of CNC for industry
CNC plays a decisive role in modern production. Automation, high accuracy and speed of production make it an indispensable tool for many industries. From the manufacture of metal parts to the creation of complex prototypes - the CNC axis helps to create the future and optimize production processes. This ultimately leads to improving the quality of products and reducing costs.
AppropriateProducts
Corresponding products
The best soldproducts
The best -selling products-
 Taisin Metal 3D printer IDEN160
Taisin Metal 3D printer IDEN160 -
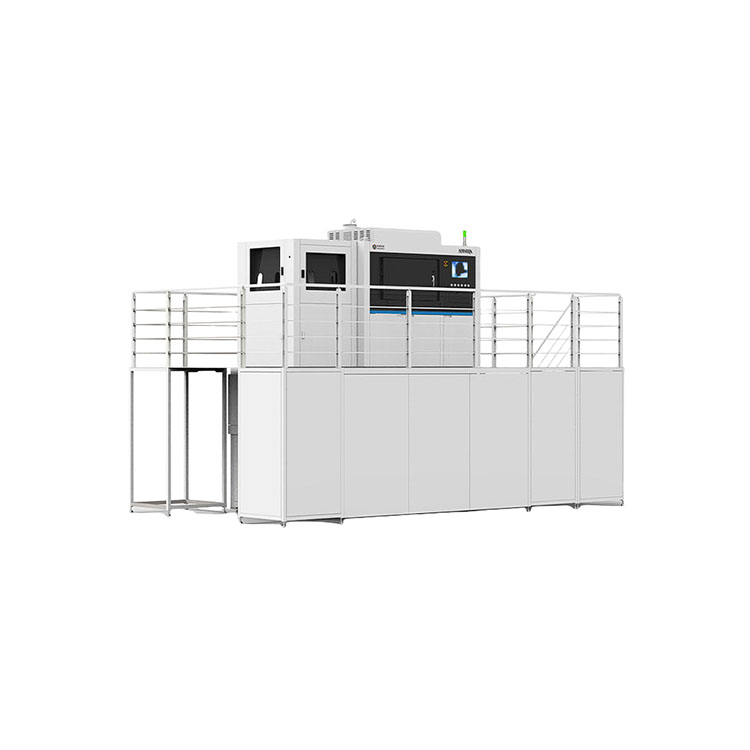 Taisin Metal 3D printer ISLM800QN
Taisin Metal 3D printer ISLM800QN -
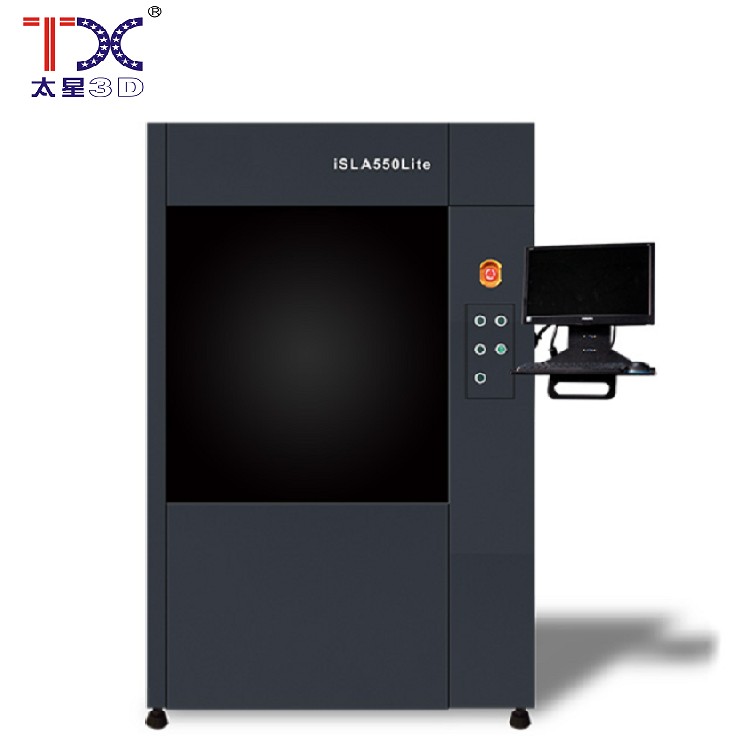 Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA550Lite
Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA550Lite -
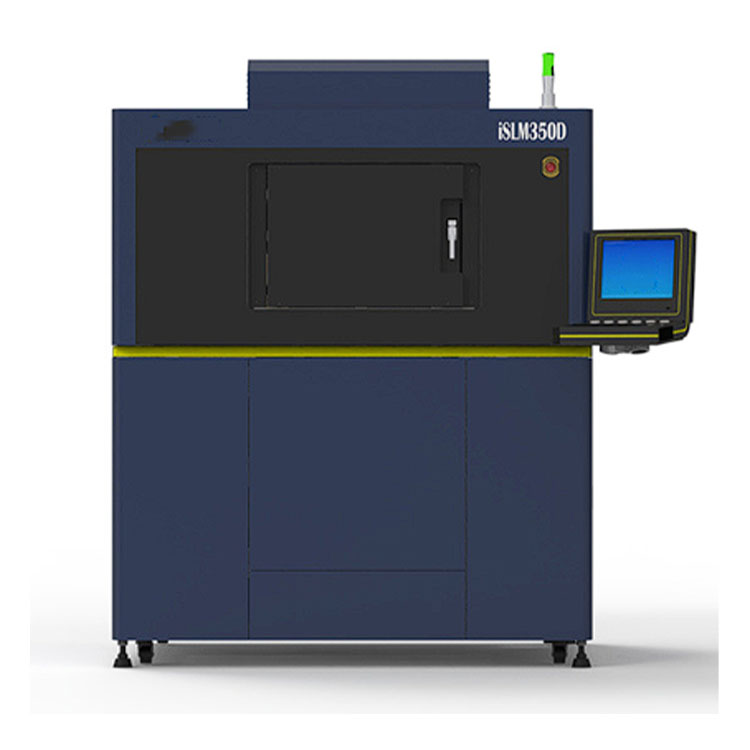 Taisin Metal 3D printer ISLM350D
Taisin Metal 3D printer ISLM350D -
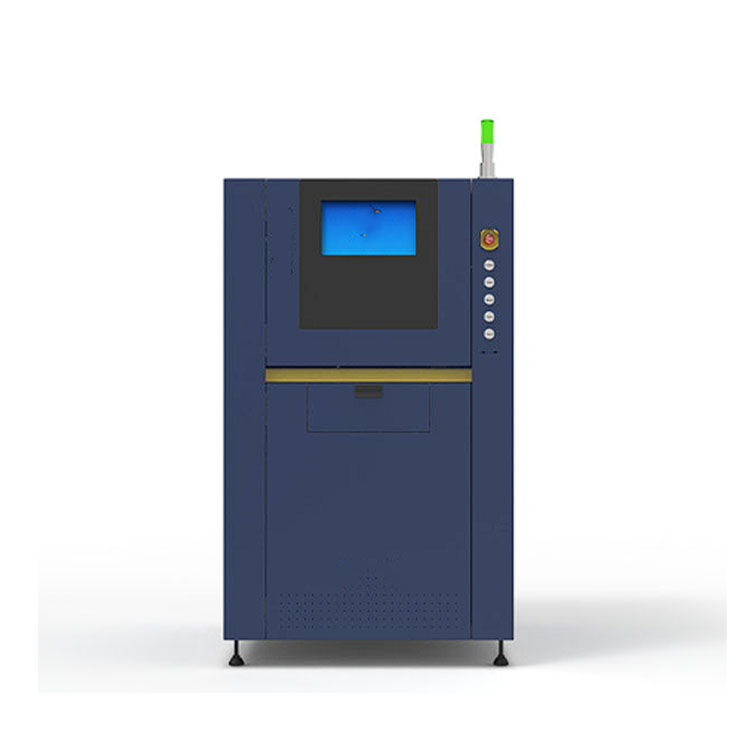 Taisin Metal 3D printer SLM160
Taisin Metal 3D printer SLM160 -
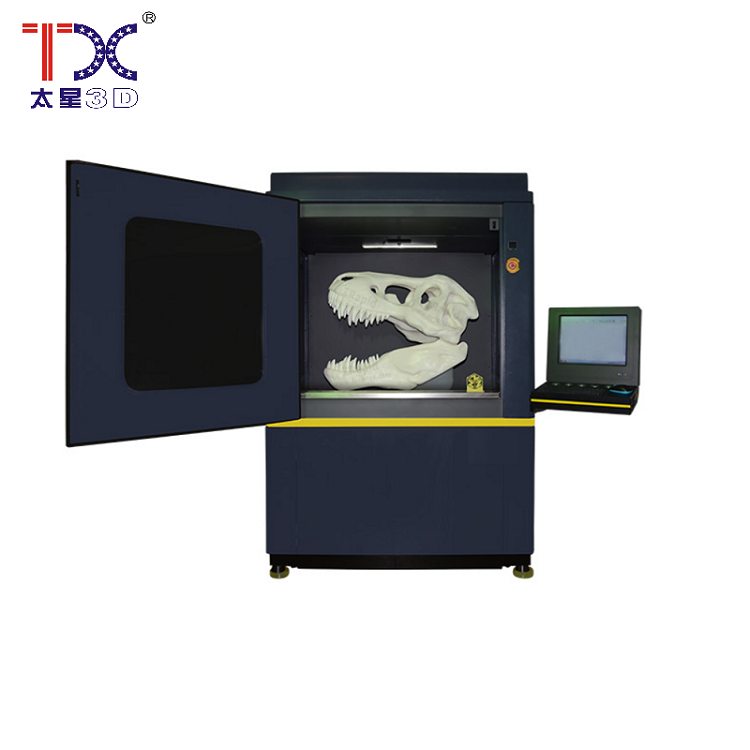 Taisin Light-adopted 3D printer ISL1100
Taisin Light-adopted 3D printer ISL1100 -
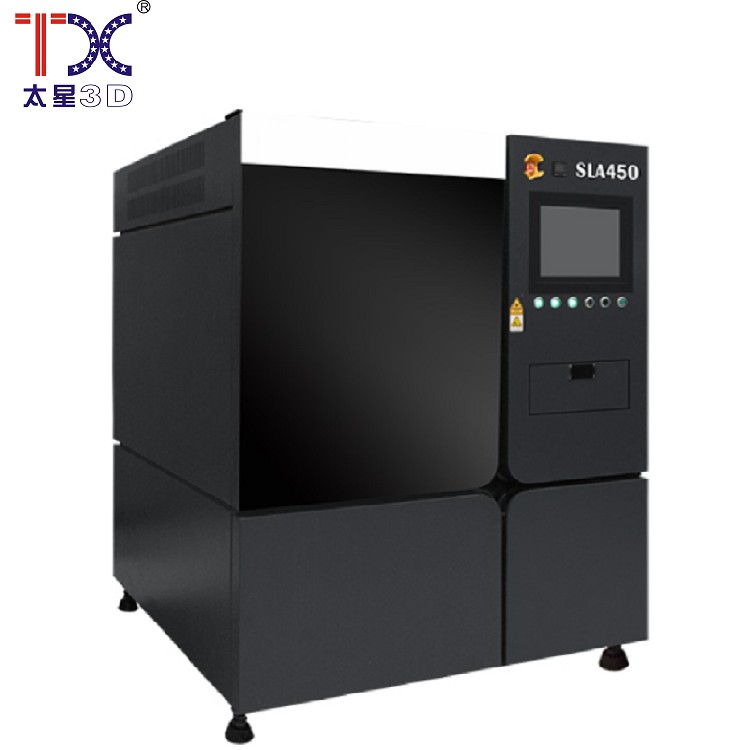 Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA450
Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA450 -
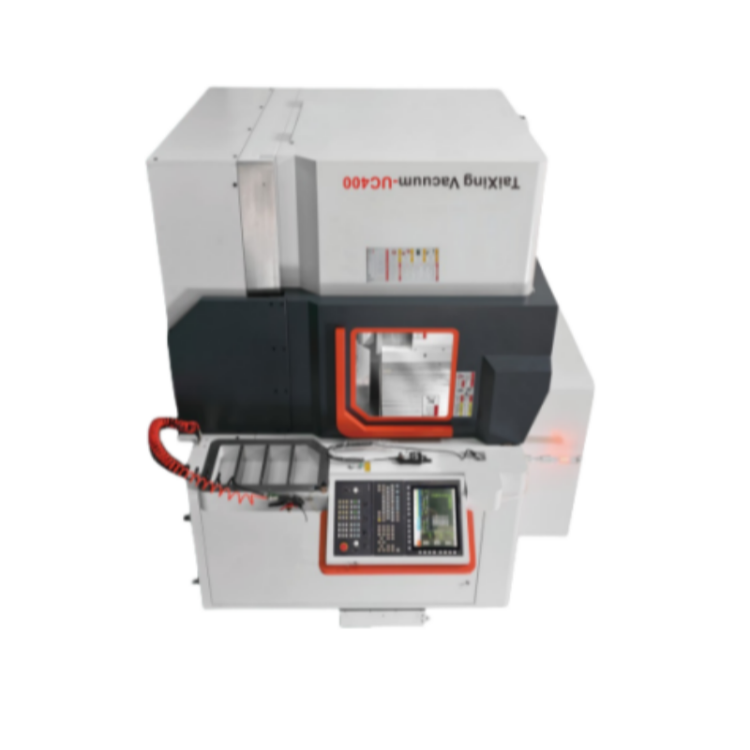 Taisin high-speed five-axis processing center TX-UC400
Taisin high-speed five-axis processing center TX-UC400 -
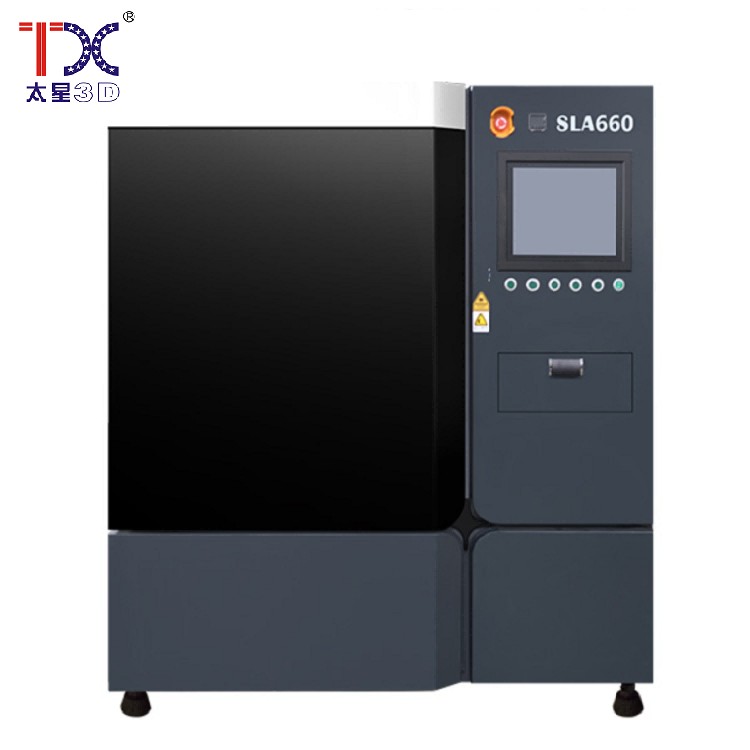 Taisin Light-adopted 3D printer SLA660
Taisin Light-adopted 3D printer SLA660 -
 Taisin Metal 3D printer ISLM600QN
Taisin Metal 3D printer ISLM600QN -
 Taisin Light-adopted 3D printer SLA660Lite
Taisin Light-adopted 3D printer SLA660Lite -
 Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA800
Taisin Light-adoptive 3D printer SLA800
Connectedsearch
Related search- Cheap manufacturers of Sketchup
- 3D printing
- Cheap 2 axes of CNC machines suppliers
- OEM suppliers of processing centers with CNC
- Cheap shafts of CNC machines suppliers
- Cheap 3D printing elimination suppliers
- Cheap 12 CNCs CNC machines manufacturers
- 3D printing manufacturers in China
- Cheap metal powders factories
- Chinese manufacturers of strong axes for CNC machines












